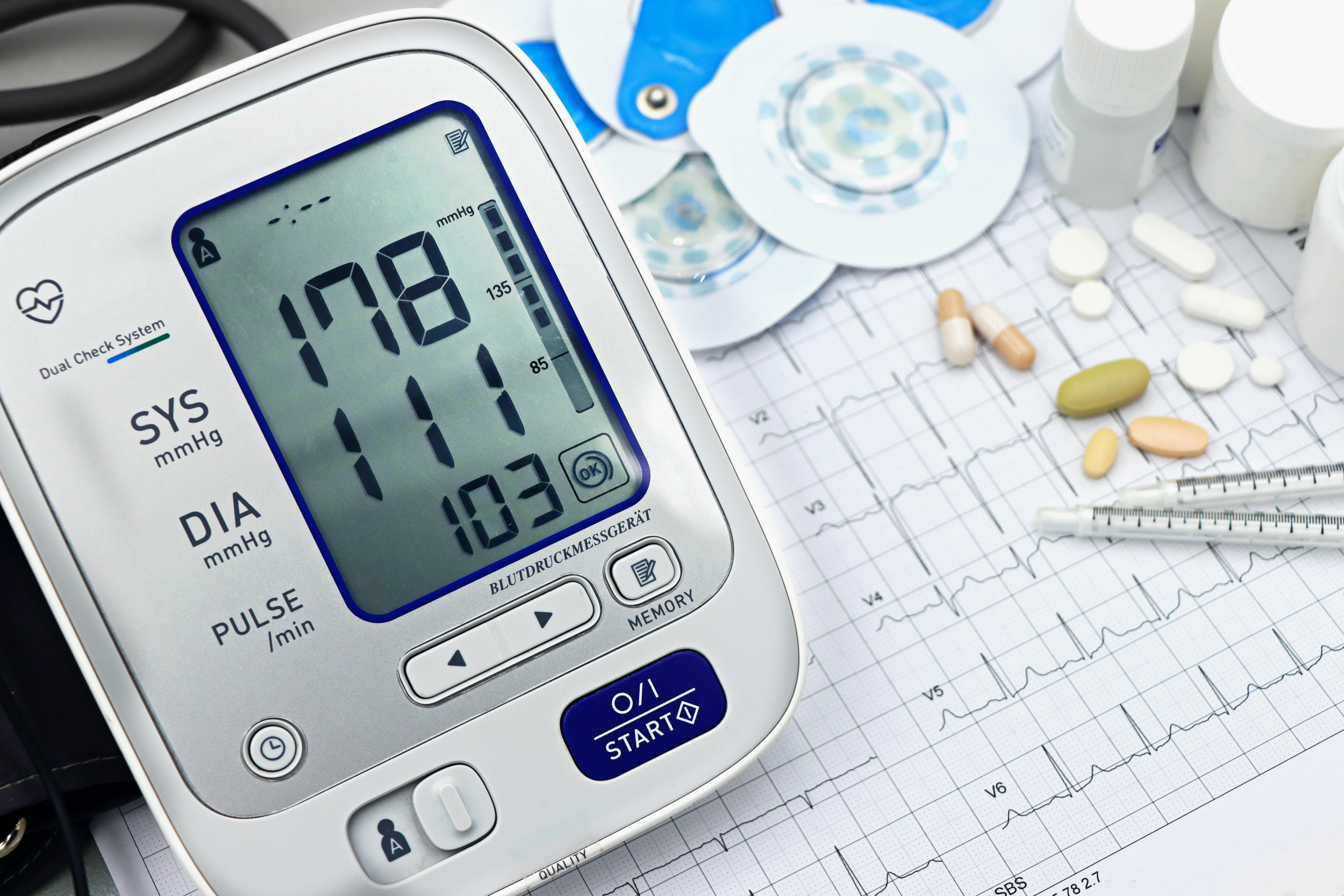
Elevated blood pressure frequently advances without any obvious indicators, solidifying its status as a stealthy danger to overall well-being that hinders efforts to safeguard cardiovascular health. Countless individuals go through their days with higher-than-normal measurements, oblivious to the ongoing stress placed on their vascular system, which progressively heightens the chances of experiencing myocardial infarctions, cerebrovascular events, or harm to essential organs. Given that the human body seldom provides overt alerts in the initial phases, consistent evaluation of blood pressure levels stands out as a vital practice for identifying this concealed issue at an early juncture.
Measurements that exceed 130/80 mmHg by even a small margin call for immediate attention, although numerous people report feeling entirely fine as the detrimental effects build up over time. When indicators such as persistent head pain or alterations in visual perception finally emerge — assuming they do — the vascular structures might already have suffered considerable deterioration. Grasping the essence of this invisible peril plays a pivotal role in maintaining enduring vitality and averting catastrophic health events prior to their onset.
Why Does Elevated Blood Pressure Earn the Moniker of Silent Killer?
The designation of silent killer for high blood pressure stems from the fact that the majority of affected individuals encounter no discernible manifestations until substantial injury has already taken hold. In the preliminary phases, there are seldom any evident alerts, even while the heightened force within the circulatory system inflicts harm on arterial linings from the interior. This slow-moving deterioration results in arteries becoming thicker and more rigid absent any sensation of discomfort, persisting until the compromised structures reach a breaking point.
As noted by authoritative health bodies, elevated blood pressure might exhibit zero outward signs, yet it markedly elevates the susceptibility to cardiovascular ailments, cardiac insufficiency, and apoplectic episodes, underscoring the imperative for timely identification to facilitate proactive countermeasures. With prolonged neglect, hypertension compels the heart to exert greater effort, fostering hypertrophy of the left ventricle, whereas the minute capillaries supplying the cerebrum and renal system grow increasingly delicate. Such imperceptible transformations build up steadily, explaining why a significant number of people receive their diagnosis through standard medical evaluations or acute crises rather than through symptomatic cues.
Is It Possible to Experience Elevated Blood Pressure Without Any Noticeable Signs?
It is quite prevalent for individuals to have high blood pressure devoid of symptoms, with many sustaining hazardous levels for extended periods without any awareness. In contrast to conditions that provoke swift unease, this form of hypertension subtly burdens the vasculature and internal organs, manifesting merely faint clues like slight cephalgia or sporadic vertigo only in later stages. Such understated signals are frequently attributed to everyday stressors, exhaustion, or insufficient hydration, thereby postponing medical intervention and remedial actions.
Health organizations emphasize that hypertension typically lacks symptomatic expression, rendering systematic surveillance indispensable for prompt recognition and control. Various ecological and biological influences can obscure its advancement, which is why personal oversight proves invaluable. Devices for at-home blood pressure assessment, coupled with periodic clinical examinations, enable the observation of patterns that might evade informal scrutiny. Particular demographic groups, such as seniors and those of African descent, confront amplified vulnerabilities, making proactive and recurrent screenings essential to forestall permanent impairment. Modifications in daily routines — including curtailing sodium consumption, incorporating steady physical activity, and regulating body mass — contribute to diminishing readings and halting the covert escalation.
What Hazards Arise from Neglecting High Blood Pressure Treatment?
When left unmanaged, high blood pressure covertly erodes critical physiological frameworks well in advance of any symptomatic emergence, rendering its repercussions both extensive and profound. Across years, the vascular conduits lose flexibility and accumulate atheromatous deposits, impeding circulation to the myocardium and cerebral tissues. Consequently, this amplifies the probability of coronary occlusions, ischemic strokes, and myocardial decompensation, frequently striking without prior notice.
Insights from leading medical institutions reveal that sustained hypertension inflicts widespread arterial degradation, causing mural hypertrophy, diminished structural resilience, and predisposing to pathologies including aneurysmal dilatations and persistent renal insufficiency. The cardiac muscle adapts to the persistent overload by expanding and intensifying its contractions, ultimately compromising its operational efficacy and heightening vulnerability to congestive heart failure. Renal compromise due to unremitting hypertension disrupts glomerular purification processes, potentially culminating in end-stage renal disease, while the pressure on delicate ocular vasculature may precipitate hypertensive retinopathy and progressive visual impairment. These multifaceted threats illustrate the gravity and pervasiveness of the condition when ignored.
Strategies for Mitigating the Risks of Asymptomatic Hypertension
Approaches to handling asymptomatic high blood pressure integrate modifications in lifestyle with pharmacological interventions to fortify vascular integrity and curtail potential complications. Everyday practices, though straightforward, yield quantifiable improvements in pressure metrics, supplemented by pharmacotherapy for instances resistant to behavioral shifts alone. Continuous surveillance validates the efficacy of these measures in sustaining cardiovascular and renal wellness over the long haul.
- Nutritionally Balanced Regimen: Restrict daily sodium to below 2,300 milligrams to achieve a reduction in systolic values by approximately 5 to 6 units, thereby bolstering cardiac function.
- Consistent Physical Activity: Dedicate 30 minutes to vigorous ambulation on most days to enhance hemodynamic flow and alleviate vascular tension, replicating the benefits of certain therapeutic agents.
- Body Weight Optimization: Shed superfluous adipose tissue and minimize abdominal girth; incremental reductions in mass can substantially depress blood pressure levels.
- Pharmacological Support: Employ angiotensin-converting enzyme blockers, thiazide diuretics, or analogous agents to promote vasodilation and optimize perfusion in scenarios where behavioral adjustments fall short.
- Stress Alleviation Techniques: Engage in disciplines such as yogic practices, contemplative awareness, or meditative sessions to progressively normalize pressure readings.
- Ongoing Surveillance Protocols: Scheduled consultations and domestic sphygmomanometry facilitate adherence to optimal thresholds and early flagging of adverse deviations.
Empowering Yourself Against Concealed Hypertension Dangers
The unobtrusive character of high blood pressure necessitates vigilant preemptive measures to secure sustained physiological equilibrium. Methodical tracking, knowledgeable alterations to habits, and expert counsel form a robust bulwark against insidious vascular attrition. Intervening prior to symptomatic onset transcends mere prevention — it constitutes a vital safeguard for vitality. Through heightened consciousness and steadfast implementation of recommended protocols, a substantial portion of hypertension-related perils can be attenuated, thereby upholding an enriched existence.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How frequently should blood pressure be assessed if no discomfort is felt?
Even absent overt manifestations, hypertension may lurk and inflict detriment. Guidelines suggest annual or biannual evaluations for those with baseline normalcy. Presence of predisposing elements like hereditary predisposition or adiposity warrants augmented frequency. Domestic apparatuses furnish insightful longitudinal data complementing clinical appraisals.
2. What accounts for the absence of symptoms in numerous hypertension cases?
The condition exerts a insidious influence on arterial architecture sans nociceptive activation. Subtle internal erosions evade detection until substantial organ duress manifests. This stealth renders it a quintessential silent adversary.
3. Are lifestyle modifications genuinely effective in reducing blood pressure?
Affirmative; such adaptations yield notable declines. Sodium restriction, routine exertion, mass reduction, and tension mastery synergize effectively, often augmenting medicinal regimens to attain desired metrics. Incremental, sustained tweaks engender transformative outcomes.
4. Under what circumstances should medical consultation be sought for hypertension?
Professional evaluation is advised upon recurrent exceedances of 130/80 mmHg. Urgent intervention is mandated for readings surpassing 180/120 mmHg. Periodic engagements refine therapeutic strategies and track evolution, nipping escalations in the bud.